IXEMPRA® (ixabepilone) dosing1
The recommended dosage of IXEMPRA is 40 mg/m2 administered intravenously over 3 hours every 3 weeks
- Doses for patients with body surface area greater than 2.2 m2 should be calculated based on 2.2 m2
- The dose of IXEMPRA is the same for monotherapy and for combination therapy with capecitabine
- For certain toxicities, an initial 20% dose reduction should be made, followed by an additional 20% dose reduction if toxicities recur

For certain toxicities, an initial dose reduction of 20% should be made, followed by an additional 20% dose reduction if toxicities recur
- Patients should be evaluated during treatment by periodic clinical observation and laboratory tests, including complete blood cell counts
- Depending on the type and severity of the toxicity, patients may require treatment discontinuation or no dose adjustment; if toxicities are present, treatment should be delayed to allow recovery
- Dosing adjustment guidelines for monotherapy and combination therapy are shown in the table below
Dose adjustment for toxicities*
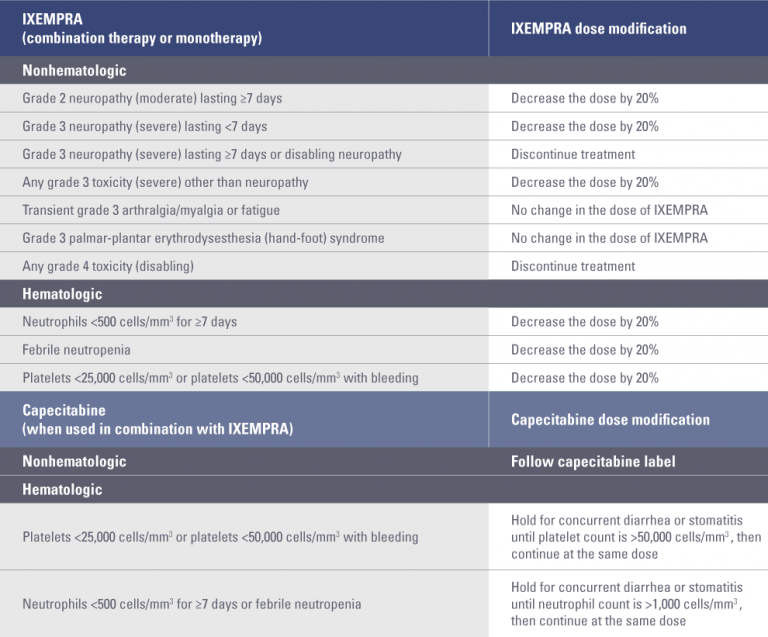
* Toxicities graded in accordance with National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) v3.0.
Re-treatment criteria1
- Dose adjustments at the start of a cycle should be based on nonhematologic toxicity or blood cell counts from the preceding cycle following the guidelines in the “Dose adjustment for toxicities” table above
- Patients should not begin a new cycle of treatment unless the neutrophil count is ≥1,500 cells/mm3, the platelet count is ≥100,000 cells/mm3, and nonhematologic toxicities have improved to grade 1 (mild) or resolved
Dose modification for patients with hepatic impairment1
- Assessment of hepatic function is recommended before initiation of IXEMPRA and periodically thereafter
- Patients with baseline AST or ALT >2.5 × ULN or bilirubin >1.5 × ULN experienced greater toxicity than patients with baseline AST or ALT ≤2.5 × ULN or bilirubin ≤1.5 × ULN when treated with IXEMPRA at 40 mg/m2 in combination with capecitabine or as monotherapy in breast cancer studies
For combination therapy
- IXEMPRA in combination with capecitabine is contraindicated in patients with AST or ALT >2.5 × ULN or bilirubin >1 × ULN
- Patients receiving combination treatment who have AST and ALT ≤2.5 × ULN and bilirubin ≤1 × ULN may receive the standard dose of IXEMPRA (40 mg/m2)
For monotherapy
- Patients with hepatic impairment should be dosed with IXEMPRA based on the table below
- Patients with moderate hepatic impairment should be started at 20 mg/m2; the dosage in subsequent cycles may be escalated up to, but should not exceed, 30 mg/m2 if tolerated
- Use in patients with AST or ALT >10 × ULN or bilirubin >3 × ULN is not recommended
- Limited data are available for patients with AST or ALT >5 × ULN; caution should be used when treating these patients
Dose adjustments for IXEMPRA monotherapy in patients with hepatic impairment
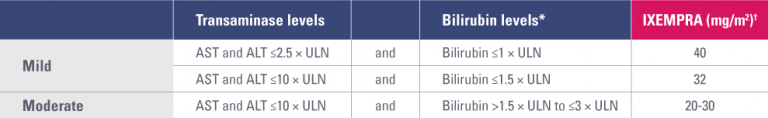
ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ULN, upper limit of normal.
* Excluding patients whose total bilirubin is elevated due to Gilbert syndrome.
† Dosage recommendations are for first course of therapy; further decreases in subsequent courses should be based on individual tolerance.
Dose modification: inhibitors and inducers of CYP3A41
CYP3A4 inhibitors
- Avoid the use of concomitant strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (eg, ketoconazole, itraconazole, clarithromycin, atazanavir, nefazodone, saquinavir, telithromycin, ritonavir, amprenavir, indinavir, nelfinavir, delavirdine, or voriconazole)
- Grapefruit juice may also increase plasma concentrations of IXEMPRA and should be avoided
- Based on pharmacokinetic studies, if a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor must be coadministered, a dose reduction to 20 mg/m2 is predicted to adjust the IXEMPRA AUC to the range observed without inhibitors and should be considered
- If the strong inhibitor is discontinued, a washout period of approximately 1 week should be allowed before the IXEMPRA dose is adjusted upward to the indicated dose
- Patients receiving CYP3A4 inhibitors during treatment with IXEMPRA should be monitored closely for acute toxicities (eg, frequent monitoring of peripheral blood cell counts between cycles of IXEMPRA)
CYP3A4 inducers
- IXEMPRA is a CYP3A4 substrate; avoid the use of concomitant strong CYP3A4 inducers (eg, phenytoin, carbamazepine, rifampin, rifabutin, dexamethasone, and phenobarbital)
- Selection of an alternative concomitant medication with no or minimal enzyme induction potential should be considered
- The following guidance may be considered for dosing in patients requiring coadministration of a strong CYP3A4 inducer if no alternatives are feasible
- Once patients have been maintained on a strong CYP3A4 inducer, the dose of IXEMPRA may be gradually increased from 40 mg/m2 to 60 mg/m2, depending on tolerance
- If the dose is increased, IXEMPRA should be given as a 4-hour intravenous infusion
- There are no clinical data with this dose adjustment in patients receiving strong CYP3A4 inducers; however, it is predicted to adjust the AUC to the range observed without inducers
- Patients whose dose is increased above 40 mg/m2 should be monitored carefully for toxicities associated with IXEMPRA
- If the strong inducer is discontinued, the IXEMPRA dose should be returned to the dose used prior to initiation of the strong CYP3A4 inducer
- St. John’s wort may decrease ixabepilone plasma concentrations unpredictably and should be avoided
Premedication1
- To minimize the chance of occurrence of a hypersensitivity reaction, all patients must be premedicated approximately 1 hour before the infusion of IXEMPRA with:
- An H1 antagonist (eg, diphenhydramine 50 mg orally or equivalent), and
- An H2 antagonist (eg, ranitidine 150-300 mg orally or equivalent)
- Patients who experienced a hypersensitivity reaction to IXEMPRA require premedication with corticosteroids (eg, dexamethasone 20 mg intravenously 30 minutes before infusion or orally 60 minutes before infusion) in addition to pretreatment with H1 and H2 antagonists
Overdosage1
- Experience with overdose of IXEMPRA is limited to isolated cases; the adverse reactions reported in these cases included peripheral neuropathy, fatigue, musculoskeletal pain/myalgia, and gastrointestinal symptoms (nausea, anorexia, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and stomatitis)
- The highest dose mistakenly received was 100 mg/m2 (total dose, 185 mg)
- There is no known antidote for overdosage of IXEMPRA; in case of overdosage, the patient should be closely monitored, and supportive treatment should be administered
- Management of overdose should include supportive medical interventions to treat the presenting clinical manifestations
Use in specific populations1
Hepatic impairment
- IXEMPRA in combination with capecitabine must not be given to patients with AST or ALT >2.5 × ULN or bilirubin >1 × ULN
- Dose reduction is recommended when administering IXEMPRA as monotherapy to patients with hepatic impairment
- Because there is a need for dosage adjustment based upon hepatic function, assessment of hepatic function is recommended before initiation of IXEMPRA and periodically thereafter
Geriatric use
- Clinical studies of IXEMPRA did not include sufficient numbers of subjects ≥65 years of age to determine whether they respond differently than younger subjects
- Forty-five of 431 patients treated with IXEMPRA in combination with capecitabine were ≥65 years of age, and 3 patients were ≥75 years of age
- Overall, the incidence of grades 3/4 adverse reactions was higher in patients ≥65 years of age versus those <65 years of age (82% vs 68%), including grades 3/4 stomatitis (9% vs 1%), diarrhea (9% vs 6%), palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia (hand-foot) syndrome (27% vs 20%), peripheral neuropathy (24% vs 22%), febrile neutropenia (9% vs 3%), fatigue (16% vs 12%), and asthenia (11% vs 6%)
- Toxicity-related deaths occurred in 2 of 43 patients (4.7%) ≥65 years of age with normal baseline hepatic function or mild impairment
- Thirty-two of 240 breast cancer patients treated with IXEMPRA as monotherapy were ≥65 years of age, and 6 patients were ≥75 years of age; no overall differences in safety were observed in these patients compared to those <65 years of age
Renal impairment
- IXEMPRA is minimally excreted via the kidney
- No controlled pharmacokinetic studies were conducted with IXEMPRA in patients with renal impairment
- IXEMPRA in combination with capecitabine has not been evaluated in patients with calculated creatinine clearance of <50 mL/min
- IXEMPRA as monotherapy has not been evaluated in patients with creatinine >1.5 × ULN
- In a population pharmacokinetic analysis of IXEMPRA as monotherapy, there was no meaningful effect of mild or moderate renal insufficiency (CrCl >30 mL/min) on the pharmacokinetics of IXEMPRA
Pregnant women and nursing mothers
- Pregnancy Category D: IXEMPRA may cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies with IXEMPRA in pregnant women. Women should be advised not to become pregnant when taking IXEMPRA. If this drug is used during pregnancy or the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus
- It is not known whether IXEMPRA is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from IXEMPRA, a decision must be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue IXEMPRA, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother
Pediatric use
- The safety and effectiveness of IXEMPRA in pediatric patients have not been established
CrCl, creatinine clearance.
AUC, area under the curve.
References: 1. IXEMPRA (ixabepilone) Prescribing Information; January 2016.
